Databinding 在2015年7月发布的Android Studio v1.3.0 版本上引入,在2016年4月Android Studio v2.0.0 上正式支持。目前为止,已经支持双向绑定。
在android中实现 MVVM 的架构模式,Data binding 是最具代表性的框架,Google推出这一框架的原因是通过数据绑定技术可以解决界面与业务分离问题,对应的在Android中你不必再写什么findViewById()、setText(),setVisibility(),setEnabled() 或 setOnClickListener() 等方法了,可简化代码。
由于以前缺少对架构的关注和重视,虽然这个框架很早出来,但是也没有进行系统性的学习,下面就对Data binding的使用做一个总结。
添加依赖 在app下的build.gradle文件中添加
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 android { compileSdkVersion 26 buildToolsVersion "26.0.1" defaultConfig { } buildTypes { } dataBinding { enabled true } }
基础用法 定义数据对象 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class TestNormalDto private String test1; private String test2; private String test3; public TestNormalDto (String test1, String test2, String test3) this .test1 = test1; this .test2 = test2; this .test3 = test3; } public String getTest1 () return test1; } public void setTest1 (String test1) this .test1 = test1; } public String getTest2 () return test2; } public void setTest2 (String test2) this .test2 = test2; } public String getTest3 () return test3; } public void setTest3 (String test3) this .test3 = test3; } }
布局文件 在 DataBinding 中,xml 的布局文件就不再单纯的展示UI,还需要定义 UI用到的变量,将变量直接与UI捆绑,个人认为类似于web开发的响应式写法。所以,它的根节点不再是一个 ViewGroup,而是变成了·layout标签的节点,并且新增了一个节点data,布局文件如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <data > <variable name ="testNormalDto" type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.dto.TestNormalDto" /> </data > <LinearLayout android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:orientation ="vertical" > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView3" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{testNormalDto.test1}" /> <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{testNormalDto.test2}" /> <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{testNormalDto.test3}" /> </LinearLayout > </layout >
吐槽一下,android studio的XML支持并不是很好,输入变量很多时候没有智能提示。这里我们引用了testNormalDto这个数据集,并将这个数据集的属性与具体的ui控件做了捆绑,在定义变量的同时,框架会自动为我们生成testNormalDto这个数据集的set方法。当我们到Activity中刷新这个数据集时,对应捆绑的控件也会跟着刷新。具体的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 ActivityMainBinding binding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView( this , R.layout.activity_main); TestNormalDto testNormalDto = new TestNormalDto("fei" , "Liang" ,"sss" ); binding.setTestNormalDto(testNormalDto);
ActivityMainBinding是DataBinding这个框架自动生成的,初始化时绑定当前的ui布局。创建一个model对象,注入到ActivityMainBinding的对象中,即可完成数据刷新操作。刷新model对象的同时刷新ui。MVVM 的 ViewModel 需要把数据(Model)与 UI(View) 进行绑定,data 节点就是连接它们之间的一个桥梁。
variable类型 variable同样支持基本数据类型,比如String,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <data > <variable name ="myStr" type ="String" /> </data > <LinearLayout android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:orientation ="vertical" > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView4" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{myStr}" /> </LinearLayout > </layout >
框架也会自动为我们生成set方法,刷新数据集的同时刷新控件显示的数据。
1 2 3 ActivityMainBinding binding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView( this , R.layout.activity_main); binding.setMyStr("测试字符串变量" );
Integer, Float,Double也同样支持,不过这里不能直接显示在控件中,要转String再显示,DataBinding的数据绑定支持表达式,我们可以先定义一个工具类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class MyStringUtils public static String convert (final Double myDouble) return myDouble+"" ; } public static String convert (final Integer myInteger) return myInteger+"" ; } public static String convert (final Float myFloat) return myFloat+"" ; }
接下来是在XML中定义变量并绑定,同样,框架会自动为我们生成set方法,这里我们在绑定的时候调用这个工具类转String再显示到控件中,注意调用工具类需要先import工具类到xml中,我们需要在<data>标签中添加<import>标签。代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <data > <import type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.dto.MyStringUtils" /> <variable name ="myInt" type ="Integer" /> <variable name ="myDouble" type ="Double" /> <variable name ="myFloat" type ="Float" /> </data > <LinearLayout android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:orientation ="vertical" > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView5" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{MyStringUtils.convert(myInt)}" /> <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView6" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{MyStringUtils.convert(myDouble)}" /> <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView7" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{MyStringUtils.convert(myFloat)}" /> </LinearLayout > </layout >
在Activity中刷新数据集,同时刷新控件显示数据
1 2 3 4 5 ActivityMainBinding binding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView( this , R.layout.activity_main); binding.setMyFloat(12.3f ); binding.setMyDouble(12.4 ); binding.setMyInt(10 );
自定义Binding的名称 除了使用自动生成的Binding名ActivityMainBinding以外,还可以在data标签中添加class属性
1 2 <data class ="CustomBinding" > </data >
类型别名 如果此时项目根目录下也存在一个TestNormalDto,这时存在两个TestNormalDto,XML中需要引入这两个dto做数据捆绑,这时data 节点了导入了两个同名的类:
1 2 3 <import type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.dto.TestNormalDto" /> <import type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.TestNormalDto" /> <variable name ="testNormalDto" type ="TestNormalDto" />
import 还有一个 alias 属性,可解决同名类问题
1 2 3 <import type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.dto.TestNormalDto" /> <import type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.TestNormalDto" alias ="NormalDto" /> <variable name ="normalDto" type ="NormalDto" />
非空判断 感觉类似java的三目运算符
1 android:text="@{user.displayName ?? user.lastName}"
这个等价于
1 android:text="@{user.displayName != null ? user.displayName : user.lastName}"
设置属性 如果TestNormalDto中添加一个属性isNormal,当该属性为true时,控件可见否则控件不可见,我们可以直接把 Java 中定义的属性值赋值给 xml 属性。
1 2 3 4 5 <TextView android:text ="@{testNormalDto.test1}" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:visibility ="@{testNormalDto.isNormal ? View.VISIBLE : View.GONE}" />
使用资源 padding的大小通过屏幕尺寸自适应,大尺寸使用dimen资源中的largePadding,否则使用smallPadding。字符串引用也可使用占位符传参的形式。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <data > <variable name ="large" type ="boolean" /> <variable name ="goodsName" type ="String" /> <variable name ="price" type ="double" /> </data > <LinearLayout android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:orientation ="vertical" > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView8" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:padding ="@{large? (int)@dimen/largePadding : (int)@dimen/smallPadding}" android:text ="@{@string/nameFormat(goodsName,price)}" /> </LinearLayout > </layout > <resources > <string name ="nameFormat" > %1$s的价格是%2$.2f</string > </resources >
同样在Activity中刷新数据集
1 2 3 4 ResourceBinding binding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView( this , R.layout.activity_main); binding.setGoodsName("T-shirt" ); binding.setPrice(15 );
context引用 context是dataBinding通过variable标签默认帮我们定义好了,该context的值就是从当前布局文件中的根节点view的getContext()方法获取的.所以我们可以在布局中直接引用context
如果我们自己通过variable标签定义了一个name为context的变量,那么会覆盖掉系统提供的context。
ViewStubs的使用 XML布局中添加
1 2 3 4 5 <ViewStub android:id ="@+id/view_stub" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:layout ="@layout/inflate_content" />
inflate_content.xml代码与activity的布局文件大致相似,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <data class ="ViewStubBinding" > <variable name ="viewStubTag" type ="String" /> </data > <LinearLayout android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:orientation ="vertical" > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{viewStubTag}" /> </LinearLayout > </layout >
在activity中inflate布局,并且增加inflate监听
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 binding.viewStub.setOnInflateListener(new ViewStub.OnInflateListener() { @Override public void onInflate (ViewStub stub, View inflated) ViewStubBinding binding = DataBindingUtil.bind(inflated); binding.setViewStubTag("这是inflate的布局" ); } }); inflateViewStub(binding); public void inflateViewStub (ActivityMainBinding binding) if (!binding.viewStub.isInflated()) { binding.viewStub.getViewStub().inflate(); } }
include的使用 XML布局中添加
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <variable name ="includeTag" type ="String" /> <include layout ="@layout/include_content" bind:includeTag ="@{includeTag}" />
include_content布局中接收由activity布局传过来的数据代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <data > <variable name ="includeTag" type ="String" /> </data > <LinearLayout android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:orientation ="vertical" > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{includeTag}" /> </LinearLayout > </layout >
在activity中加一句代码即可传入数据
1 binding.setIncludeTag("这是include的内容" );
@BindingConversion与@BindingAdapter XML布局中添加
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <variable name ="isNormal" type ="boolean" /> <variable name ="height" type ="float" /> <variable name ="time" type ="java.util.Date" /> <TextView android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="50dp" android:background ="@{isNormal ? @color/colorPrimary : @color/colorAccent}" android:gravity ="center" bind:custom ="@{height}" /> <TextView android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{time}" />
在activity中添加绑定代码,bind:custom这个是我们自定义的属性,databinding会去查找自定义的setCustom的方法,需要添加注解@BindingAdapter,第一个参数必须是我们需要刷新的控件类型,第二个参数就是传入到我们自定义属性中的数据,这里我们传入的是float类型的高度值,我们可以根据这个高度值动态设置控件的高度。
在activity中添加绑定代码,android:text属性的目标类型是String,但是这里我们定义的是一个Date变量,传入后不能直接使用,所以我们需要在显示之前做一次转化,就像服务器给我们int型的数据,但是我们显示时,往往需要根据状态值显示string类型。添加注解@BindingConversion,传入我们定义的类型Date,转化为可显示的String类型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @BindingConversion public static String convertDate (Date date) SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd" ); if (date!=null ){ return sdf.format(date); }else { return "" ; } } @BindingAdapter ("custom" )public static void setCustom (TextView textView, float height) ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = textView.getLayoutParams(); params.height = (int ) height; textView.setLayoutParams(params); }
最后在activity中刷新数据
1 2 3 binding.setIsNormal(false ); binding.setHeight(400 ); binding.setTime(new Date());
Recyclerview的动态绑定 只需获得item布局对应的binding对象,然后刷新数据即可,感觉与ButterKnife的使用方法类似。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 public class ListAdapter extends RecyclerView .Adapter <ListAdapter .ListHolder > private static final int BEANS_COUNT = 10 ; @NonNull private List<Bean> beans; public ListAdapter () beans = new ArrayList<>(10 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < BEANS_COUNT; i ++) { Bean bean = new Bean("测试数据" +i,i); beans.add(bean); } } public static class ListHolder extends RecyclerView .ViewHolder private BeanItemBinding binding; public ListHolder (View itemView) super (itemView); binding = DataBindingUtil.bind(itemView); } public void bind (@NonNull Bean bean) binding.setBean(bean); } } @Override public ListHolder onCreateViewHolder (ViewGroup viewGroup, int i) View itemView = LayoutInflater.from(viewGroup.getContext()) .inflate(R.layout.bean_item, viewGroup, false ); return new ListHolder(itemView); } @Override public void onBindViewHolder (ListHolder holder, int position) holder.bind(beans.get(position)); } @Override public int getItemCount () return beans.size(); } }
Bean类的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Bean private String name; private int position; public Bean (String name, int position) this .name = name; this .position = position; } public String getName () return name; } public void setName (String name) this .name = name; } public int getPosition () return position; } public void setPosition (int position) this .position = position; } }
item_bean.xml中定义bean对象,并将属性与控件捆绑的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <data class ="BeanItemBinding" > <import type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.dto.MyStringUtils" > </import > <variable name ="bean" type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.dto.Bean" > </variable > </data > <RelativeLayout android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:orientation ="vertical" > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textName" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:layout_marginLeft ="10dp" android:text ="@{bean.name}" /> <TextView android:id ="@+id/textPosition" android:layout_alignParentRight ="true" android:layout_marginRight ="10dp" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{MyStringUtils.convert(bean.position)}" /> </RelativeLayout > </layout >
最后在activity中初始化recyclerview
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class RecyclerviewActivity extends AppCompatActivity private RecyclerView recyclerView; private ListAdapter adapter; @Override protected void onCreate (@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) super .onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_recyclerview); recyclerView= (RecyclerView) this .findViewById(R.id.recyclerview); recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this )); adapter=new ListAdapter(); recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter); } }
Observable Binding配合实现双向绑定 Observable Binding有三种实现方式:
继承BaseObservable类
实现Observable接口
使用Observable封装的响应式对象
Observable Binding具体表现主要是在数据源发生改变时,自动通知view刷新数据。
BaseObservable是双向绑定的基础
结合双向绑定表达式@={},可以做到当view内容变化时,自动通知数据源更新。
继承BaseObservable类实现 我们需要在DTO类继承BaseObservable类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class ObservableBean extends BaseObservable private String test1; @Bindable public String getTest1 () return test1; } public void setTest1 (String test1) this .test1 = test1; notifyPropertyChanged(BR.test1); } }
与以往不同的是,需要用@Bindable注解get方法,在set方法最后一行添加notifyPropertyChanged方法,通知数据刷新。
在xml布局文件中对相应控件进行数据绑定,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <data > <variable name ="observableBean" type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.dto.ObservableBean" > </variable > </data > <LinearLayout android:orientation ="vertical" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textObservable" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{observableBean.test1}" /> <EditText android:id ="@+id/editObservable" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@={observableBean.test1}" /> </LinearLayout > </layout >
注意,此时EditText的text赋值为@={xxx}就是在调用双向绑定,根据我们当前输入的字符串去刷新数据源,然后数据源再刷新对应的控件,我们可以在TextView中绑定相同的字段查看数据源中的字段是否同步更新。这里有个死循环的问题,需要对旧数据和新数据作比较,如果相同则是会引起死循环的重复刷新,是需要过滤掉的,不过EditText作为系统组件,databinding的框架中已经解决了。
在activity中刷新数据,跟以前没有区别,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 observableBean=new ObservableBean(); observableBean.setTest1("测试数据1" ); ActivityObervableBinding binding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView( this , R.layout.activity_obervable); binding.setObservableBean(observableBean); EditText editObservable=findViewById(R.id.editObservable); editObservable.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() { @Override public void beforeTextChanged (CharSequence charSequence, int i, int i1, int i2) } @Override public void onTextChanged (CharSequence charSequence, int i, int i1, int i2) } @Override public void afterTextChanged (Editable editable) Log.d(TAG, "afterTextChanged: " +observableBean.getTest1()); } );
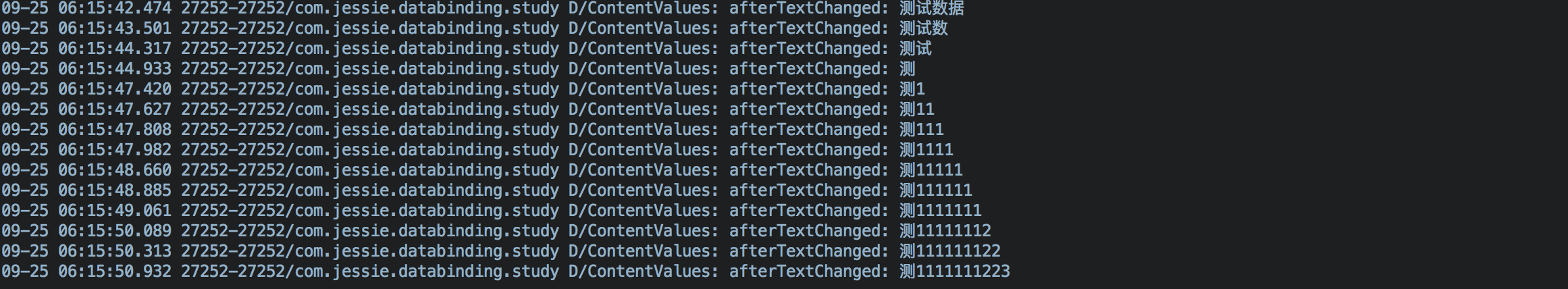
我们也可以通过EditText的监听去打印数据源,效果图和截图如下:
EditText中输入的效果图:
log打印出的截图:
这里可能会出现一个问题,我们的实体类已经继承了其他父类,不能再继承BaseObservable。第二种实现方式可以解决这个问题
实现Observable接口 只有DTO类需要修改,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class ObservableImpBean implements Observable private PropertyChangeRegistry registry =new PropertyChangeRegistry(); private String test1; @Bindable public String getTest1 () return test1; } public void setTest1 (String test1) this .test1 = test1; registry.notifyChange(this , BR.test1); } @Override public void addOnPropertyChangedCallback (OnPropertyChangedCallback callback) registry.add(callback); } @Override public void removeOnPropertyChangedCallback (OnPropertyChangedCallback callback) registry.remove(callback); } }
我们需要先实例化PropertyChangeRegistry对象,实现Observable接口必须实现addOnPropertyChangedCallback方法和removeOnPropertyChangedCallback方法,我们用PropertyChangeRegistry对象分别调用对应的add方法和remove方法传入callback即可,同样需要用@Bindable注解get方法,在set方法最后一行添加PropertyChangeRegistry对象调用notifyChange方法,通知数据刷新。事实上,BaseObservable也是实现了Observable这个接口。
最后一种常见情况,我们的实体类的字段很多很多,要是每个get/set方法都对应加上@Bindable注解和notifyPropertyChanged()方法,显得很麻烦,那么第三个方式可以解决这个问题
使用Observable封装的响应式对象 我们需要修改DTO类,代码如下:
1 2 3 public class ObservableObject public final ObservableField<String> test1 = new ObservableField<>(); }
这里用到了DataBinding提供的响应式对象,看起来是不是精简许多了呢?
基本类型的数据结构提的包装类
ObservableBoolean
ObservableByte
ObservableChar
ObservableDouble
ObservableFloat
ObservableInt
ObservableLong
ObservableShort
针对集合提供的包装类
ObservableArrayList
ObservableArrayMap
针对实现了Parcelable接口的对象提供的包装类
针对其他类型提供的包装类
ObservableField。最典型的:ObservableField
接下来是在xml中绑定对应的控件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <variable name ="observableObject" type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.dto.ObservableObject" > </variable > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textObservable2" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@{observableObject.test1.get()}" /> <EditText android:id ="@+id/editObservable2" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="@={observableObject.test1.get()}" />
我们可以看到包装类的set,get方法略有不同。
1 2 3 observableObject=new ObservableObject(); observableObject.beanField.set("测试响应式对象" ); binding.setObservableObject(observableObject);
最后注意一点,并不是只靠BaseObservable加上双向绑定表达式@={}就可以实现双向绑定。实际上在使用双向绑定时,还得依靠各个注解的帮助,监听view内容的变化是BaseObservable做不到的,需要依赖指定的注解才能把view内容的变化通知出去,然后BaseObservable收到这些通知后触发 notifyPropertyChanged(),改变数据源以及界面。而这些对于android自带的组件DataBinding已经处理好了,所以对于自定义的控件需要自己通过这些注解实现双向绑定。
MVPVM实战 自从google推出databinding后,View Interface的部分功能可以转移到ViewModel中去,进一步降低View层的臃肿。结合已经比较流行的MVP架构,衍生出一种新的架构,叫做MVPVM。MVPVM=Model+View+Presenter+ViewModel
除ViewModel层外,其余与MVP大致相同,各个分层的主要职责:
View层:实现View Interface,对外提供UI操作的方法,比如界面显示刷新,弹窗,消息提示。
ViewModel层:以databinding为基础,对外提供控制xml界面的方法。
Presenter层:实现Presenter Interface,调用model层处理业务逻辑并显示到View层上。
Model层:处理业务逻辑,如数据请求,缓存处理,数据库处理。
前一篇在介绍Dagger的时候写过登录功能,这里就登录功能以MVPVM的架构再写一个小例子。
dto为响应式对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class User extends BaseObservable public ObservableField<String> username=new ObservableField<>(); public ObservableField<String> password=new ObservableField<>(); public ObservableInt usernamePass=new ObservableInt(); public ObservableInt passwordPass=new ObservableInt(); }
M层没有什么变化
M层接口
1 2 3 4 5 public interface ILoginModel public boolean login (String username, String password) public boolean checkUserName (String username) public boolean checkPassword (String password) }
M层实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class LoginModel implements ILoginModel public LoginModel () } @Override public boolean login (String username,String password) if ("admin" .equals(username)&&"123456" .equals(password)){ return true ; }else { return false ; } } @Override public boolean checkUserName (String username) if ("admin" .equals(username)){ return true ; }else { return false ; } } @Override public boolean checkPassword (String password) if ("123456" .equals(password)){ return true ; }else { return false ; } } }
P层需要传入V层接口,初始化响应式对象,并提供获取接口,响应式对象必须在V层绑定。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 public class LoginPresenter private ILoginModel iLoginModel; private ILoginView iLoginView; private User user; public LoginPresenter (ILoginView iLoginView) iLoginModel = new LoginModel(); user=new User(); this .iLoginView=iLoginView; } public User getUser () return user; } public void checkPassword () if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(user.password.get())){ if (iLoginModel.checkPassword(user.password.get())) { user.passwordPass.set(1 ); }else { user.passwordPass.set(2 ); } }else { user.passwordPass.set(0 ); } } public void checkUserName () if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(user.username.get())){ if (iLoginModel.checkUserName(user.username.get())){ user.usernamePass.set(1 ); }else { user.usernamePass.set(2 ); } }else { user.usernamePass.set(0 ); } } public void login () if (iLoginModel.login(user.username.get(),user.password.get())){ iLoginView.onLoginResult(true ); }else { iLoginView.onLoginResult(false ); } } }
V层接口,代码如下:
1 2 3 public interface ILoginView public void onLoginResult (boolean result) }
V层实现代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 public class LoginActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements ILoginView private static final String TAG = "LoginActivity" ; private LoginPresenter loginPresenter; EditText et_username,et_password; TextInputLayout usernameInput; TextInputLayout passwordInput; User user; ActivityLoginBinding activityLoginBinding; @Override protected void onCreate (@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) super .onCreate(savedInstanceState); activityLoginBinding= DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this ,R.layout.activity_login); loginPresenter=new LoginPresenter(this ); user=loginPresenter.getUser(); activityLoginBinding.setUser(user); et_username= (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_username); et_password= (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_password); usernameInput = (TextInputLayout) findViewById(R.id.usernameInput); passwordInput = (TextInputLayout) findViewById(R.id.passwordInput); et_username.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() { @Override public void beforeTextChanged (CharSequence charSequence, int i, int i1, int i2) } @Override public void onTextChanged (CharSequence charSequence, int i, int i1, int i2) } @Override public void afterTextChanged (Editable editable) loginPresenter.checkUserName(); } }); et_password.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() { @Override public void beforeTextChanged (CharSequence charSequence, int i, int i1, int i2) } @Override public void onTextChanged (CharSequence charSequence, int i, int i1, int i2) } @Override public void afterTextChanged (Editable editable) Log.d(TAG, "afterTextChanged: " +user.password.get()); loginPresenter.checkPassword(); } }); } public void onLoginClick (View view) hideKeyboard(); loginPresenter.login(); } public void hideKeyboard () View view = getCurrentFocus(); if (view != null ) { ((InputMethodManager) getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE)). hideSoftInputFromWindow(view.getWindowToken(), InputMethodManager.HIDE_NOT_ALWAYS); } } @BindingAdapter ("onUsernameChange" ) public static void setOnUsernameChange (TextInputLayout usernameInput, int result) if (result==0 || result==1 ){ usernameInput.setErrorEnabled(false ); } else { usernameInput.setError("用户名无效!" ); } } @BindingAdapter ("onPasswordChange" ) public static void setOnPasswordChange (TextInputLayout passwordInput, int result) if (result==0 || result==1 ){ passwordInput.setErrorEnabled(false ); }else { passwordInput.setError("密码无效!" ); } } @Override public void onLoginResult (boolean result) if (result){ Toast.makeText(this ,"登录成功!" ,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }else { Toast.makeText(this ,"登录失败!" ,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } } }
此处EditText使用了databinding的双向绑定,在输入用户名和密码的同时,刷新数据源。P层调用M层校验用户名密码状态,并结果返回到P层。TextInputLayout使用了@BindingAdapter注解绑定自定义属性,setOnUsernameChange方法绑定onUsernameChange属性,传入目标view和自定义属性的值,根据用户名的校验状态,设置对应TextInputLayout的错误提示。同样,setOnPasswordChange方法绑定onPasswordChange属性,传入目标view和自定义属性的值,根据密码的校验状态,设置对应TextInputLayout的错误提示。所以V层接口只需要提供登录成功后的提示接口。
LoginActivity的XML布局代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:bind ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" > <data > <variable name ="user" type ="com.jessie.databinding.study.mvpvm.dto.User" > </variable > </data > <android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:app ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools ="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" > <android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout android:id ="@+id/usernameInput" android:layout_width ="0dp" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom ="52dp" android:layout_marginEnd ="8dp" android:layout_marginLeft ="8dp" android:layout_marginRight ="8dp" android:layout_marginStart ="8dp" android:layout_marginTop ="8dp" bind:onUsernameChange ="@{user.usernamePass}" app:errorTextAppearance ="@style/Theme.AppCompat" app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf ="@+id/passwordInput" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias ="1.0" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf ="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf ="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf ="parent" app:layout_constraintVertical_bias ="1.0" tools:layout_constraintLeft_creator ="1" tools:layout_constraintRight_creator ="1" > <EditText android:id ="@+id/et_username" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:hint ="Username" android:text ="@={user.username}" android:inputType ="textEmailAddress" tools:layout_editor_absoluteX ="8dp" tools:layout_editor_absoluteY ="28dp" /> </android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout > <android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout android:id ="@+id/passwordInput" android:layout_width ="0dp" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:layout_below ="@id/usernameInput" android:layout_marginBottom ="257dp" android:layout_marginEnd ="8dp" android:layout_marginLeft ="8dp" android:layout_marginRight ="8dp" android:layout_marginStart ="8dp" bind:onPasswordChange ="@{user.passwordPass}" app:errorTextAppearance ="@style/Theme.AppCompat" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf ="parent" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias ="0.0" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf ="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf ="parent" tools:layout_constraintBottom_creator ="1" tools:layout_constraintLeft_creator ="1" tools:layout_constraintRight_creator ="1" > <EditText android:id ="@+id/et_password" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:hint ="Password" android:text ="@={user.password}" android:inputType ="textPassword" tools:layout_editor_absoluteY ="74dp" /> </android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout > <Button android:id ="@+id/button" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom ="139dp" android:onClick ="onLoginClick" android:text ="登录" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf ="parent" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf ="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf ="parent" tools:layout_constraintBottom_creator ="1" tools:layout_constraintLeft_creator ="1" tools:layout_constraintRight_creator ="1" /> <android.support.constraint.Guideline android:id ="@+id/guideline" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:orientation ="vertical" app:layout_constraintGuide_begin ="192dp" /> </android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout > </layout >
databinding的总结:
优点:解决界面与业务分离问题,简化代码,可提高开发效率。
缺点:错误提示很难定位,XML中数据捆绑的代码编辑提示不够智能。
我已经把所有例子的完整代码打包上传,想查看demo源码的朋友,这里有传送门